If you’re happy and you know it: Neural correlates of self-evaluated psychological health and well-being
Abstract
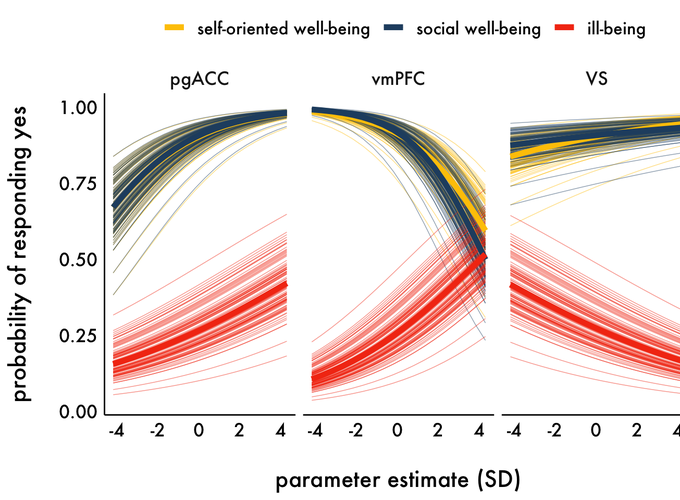
Psychological health and well-being have important implications for individual and societal thriving. Research underscores the subjective nature of well-being, but how do individuals intuit this subjective sense of well-being in the moment? This pre-registered study addresses this question by examining the neural correlates of self-evaluated psychological health and their dynamic relationship with trial-level evaluations. Participants (N = 105) completed a self-evaluation task and made judgments about three facets of psychological health and positive functioning—self-oriented well-being, social well-being and ill-being. Consistent with pre-registered hypotheses, self-evaluation elicited activity in the default mode network, and there was strong spatial overlap among constructs. Trial-level analyses assessed whether and how activity in a priori regions of interest—perigenual anterior cingulate cortex (pgACC), ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) and ventral striatum—were related to subjective evaluations. These regions explained additional variance in whether participants endorsed or rejected items but were differentially related to evaluations. Stronger activity in pgACC was associated with a higher probability of endorsement across constructs, whereas stronger activity in vmPFC was associated with a higher probability of endorsing ill-being items, but a lower probability of endorsing self-oriented and social well-being items. These results add nuance to neurocognitive accounts of self-evaluation and extend our understanding of the neurobiological basis of subjective psychological health and well-being.