Abstract
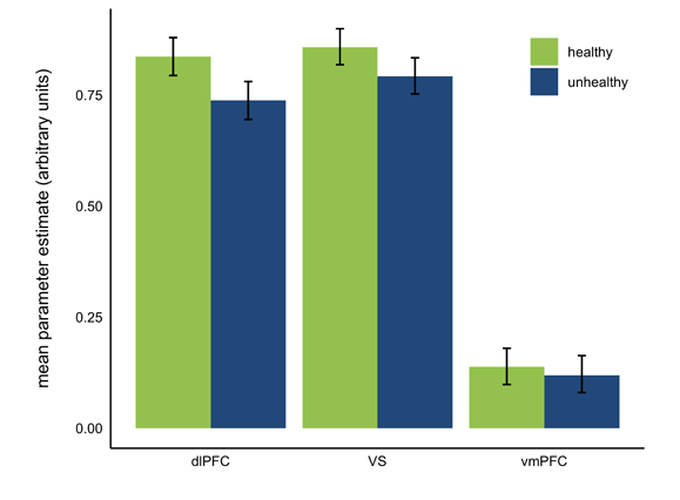
Self-control is the process of favoring abstract, distal goals over concrete, proximal goals during decision making, and is an important factor in health and well-being. We directly compare two prominent neurocognitive models of human self-control with the goal of identifying which, if either, best describes behavioral and neural data of dietary self-control decisions in a large sample of overweight and obese adults motivated to eat more healthfully. We extracted trial-by-trial estimates of neural activity during incentive-compatible choice from three brain regions implicated in self-control, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, ventral striatum, and ventromedial prefrontal cortex, and assessed evidence for the dual-process and value-based choice models of self-control using multilevel modeling. Model comparison tests revealed that the value-based choice model outperformed the dual-process model, and best fit the observed data. These results advance scientific knowledge of the neurobiological mechanisms underlying self-control and are consistent with a value-based choice model of self-control.
Citation:
Cosme, D., Ludwig, R. M., & Berkman, E. T. (2019). Comparing two neurocognitive models of self-control during dietary decisions. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 14(9), 957-966.