Mindful attention to alcohol can reduce cravings in the moment and consumption in daily life
Abstract
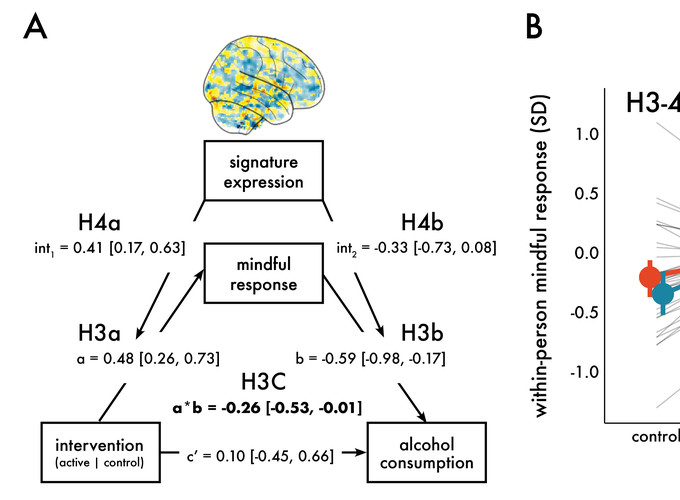
It is critical to support healthy development of alcohol-related habits, particularly in contexts with heightened risk such as college campuses. Combining multivariate neuroimaging, intervention, and experience sampling methodologies, we tested the degree to which mindful attention reduces alcohol cravings in the laboratory and consumption in daily life. College students completed a mindful attention task towards alcohol in an fMRI scanner followed by a 28-day, smartphone-based, experience sampling intervention. Using machine learning, we created a brain signature of mindful attention. In the laboratory, mindfully attending to alcohol decreased craving, particularly among people who more strongly expressed the mindful attention signature. In daily life, mindful attention to alcohol reduced alcohol consumption. Individuals who more strongly expressed the mindful attention brain signature in the laboratory benefited the most from the intervention. Broadly, our study highlights how mindful attention can reduce alcohol consumption via a scalable smartphone-based intervention.